Architecture
A Fluss cluster consists of two main processes: the CoordinatorServer and the TabletServer.
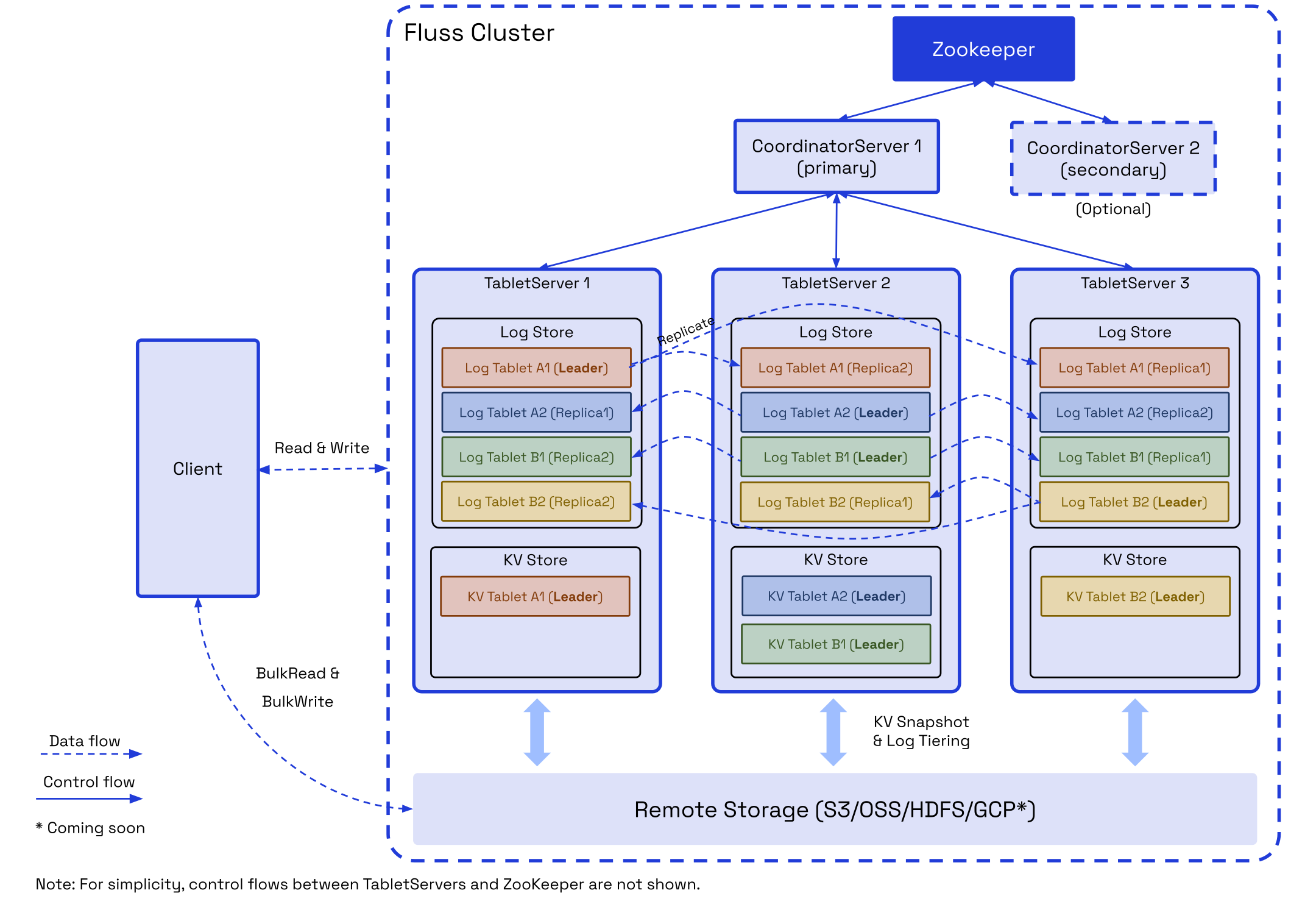
CoordinatorServer
The CoordinatorServer serves as the central control and management component of the cluster. It is responsible for maintaining metadata, managing tablet allocation, listing nodes, and handling permissions.
Additionally, it coordinates critical operations such as:
- Rebalancing data during node scaling (upscaling or downscaling).
- Managing data migration and service node switching in the event of node failures.
- Overseeing table management tasks, including creating or deleting tables and updating bucket counts.
As the brain of the cluster, the Coordinator Server ensures efficient cluster operation and seamless management of resources.
TabletServer
The TabletServer is responsible for data storage, persistence, and providing I/O services directly to users. It comprises two key components: LogStore and KvStore.
- For PrimaryKey Tables which support updates, both LogStore and KvStore are activated. The KvStore is used to support updates and point lookup efficiently. LogStore is used to store the changelogs of the table.
- For Log Tables which only supports appends, only the LogStore is activated, optimizing performance for write-heavy workloads.
This architecture ensures the TabletServer delivers tailored data handling capabilities based on table types.
LogStore
The LogStore is designed to store log data, functioning similarly to a database binlog. Messages can only be appended, not modified, ensuring data integrity. Its primary purpose is to enable low-latency streaming reads and to serve as the write-ahead log (WAL) for restoring the KvStore.
KvStore
The KvStore is used to store table data, functioning similarly to database tables. It supports data updates and deletions, enabling efficient querying and table management. Additionally, it generates comprehensive changelogs to track data modifications.
Tablet / Bucket
Table data is divided into multiple buckets based on the defined bucketing policy.
Data for the LogStore and KvStore is stored within tablets. Each tablet consists of a LogTablet and, optionally, a KvTablet, depending on whether the table supports updates.
Both LogStore and KvStore adhere to the same bucket-splitting and tablet allocation policies. As a result, LogTablets and KvTablets with the same tablet_id are always allocated to the same TabletServer for efficient data management.
The LogTablet supports multiple replicas based on the table's configured replication factor, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance. Currently, replication is not supported for KvTablets.
Zookeeper
Fluss currently utilizes ZooKeeper for cluster coordination, metadata storage, and cluster configuration management. In upcoming releases, ZooKeeper will be replaced by KvStore for metadata storage and Raft for cluster coordination and ensuring consistency. This transition aims to streamline operations and enhance system reliability. See the Roadmap for more details.
Remote Storage
Remote Storage serves two primary purposes:
- Hierarchical Storage for LogStores: By offloading LogStore data, it reduces storage costs and accelerates scaling operations.
- Persistent Storage for KvStores: It ensures durable storage for KvStore data and collaborates with LogStore to enable fault recovery.
Additionally, Remote Storage allows clients to perform bulk read operations on Log and Kv data, enhancing data analysis efficiency and reduce the overhead on Fluss servers. In the future, it will also support bulk write operations, optimizing data import workflows for greater scalability and performance.
Client
Fluss clients/sdks support streaming reads/writes, batch read/writes, DDL and point queries. Currently, the main implementation of client is Flink Connector. Users can use Flink SQL to easily operate Fluss tables and data.