ROLL Configuration System Detailed Explanation
The ROLL framework adopts a structured configuration system that defines experimental parameters through YAML files. This document will provide a detailed introduction to ROLL's configuration design, helping new users understand the framework's configuration structure and extension methods.
Configuration System Architecture
ROLL's configuration system is primarily composed of the following core components:
1. BaseConfig - Base Configuration Class
BaseConfig is the base class for all configurations, defining basic experimental parameters such as:
- Experiment name (
exp_name) - Random seed (
seed) - Output directory (
output_dir) - Log directory (
logging_dir) - Tracker configuration (
track_with,tracker_kwargs) - Training step control (
max_steps,save_steps,logging_steps,eval_steps) - Batch size (
rollout_batch_size,val_batch_size) - Sequence length settings (
prompt_length,response_length,sequence_length)
2. WorkerConfig - Worker Node Configuration Class
WorkerConfig defines the configuration for each worker node (such as training/inference roles), including:
- Model parameters (
model_args) - Training parameters (
training_args) - Data parameters (
data_args) - Generation parameters (
generating_args) - Strategy parameters (
strategy_args) - Device mapping (
device_mapping) - Number of worker nodes (
world_size)
3. PipelineConfig - Pipeline Configuration Class
In RLVR scenarios, RLVRConfig inherits from BaseConfig and serves as the configuration class for specific tasks (other PipelineConfigs include AgenticConfig, DPOConfig, DistillConfig). It includes:
- Role configurations (
actor_train,actor_infer,reference,critic,rewards, etc.) - RL algorithm-related parameters (
ppo_epochs,adv_estimator,reward_clip, etc.) - Data processing parameters (
max_len_mask,difficulty_mask, etc.)
4. Strategy - Strategy Configuration
Strategy configuration defines the training/inference strategy used by each worker node, including:
- Strategy name (such as
megatron_train,vllm,sglang,deepspeed_train, etc.) - Strategy-specific parameters (such as tensor parallel size, pipeline parallel size, etc.)
5. Arguments Classes
ROLL uses multiple argument classes to organize configurations:
ModelArguments: Model-related parametersTrainingArguments: Training-related parametersGeneratingArguments: Generation-related parametersDataArguments: Data-related parameters
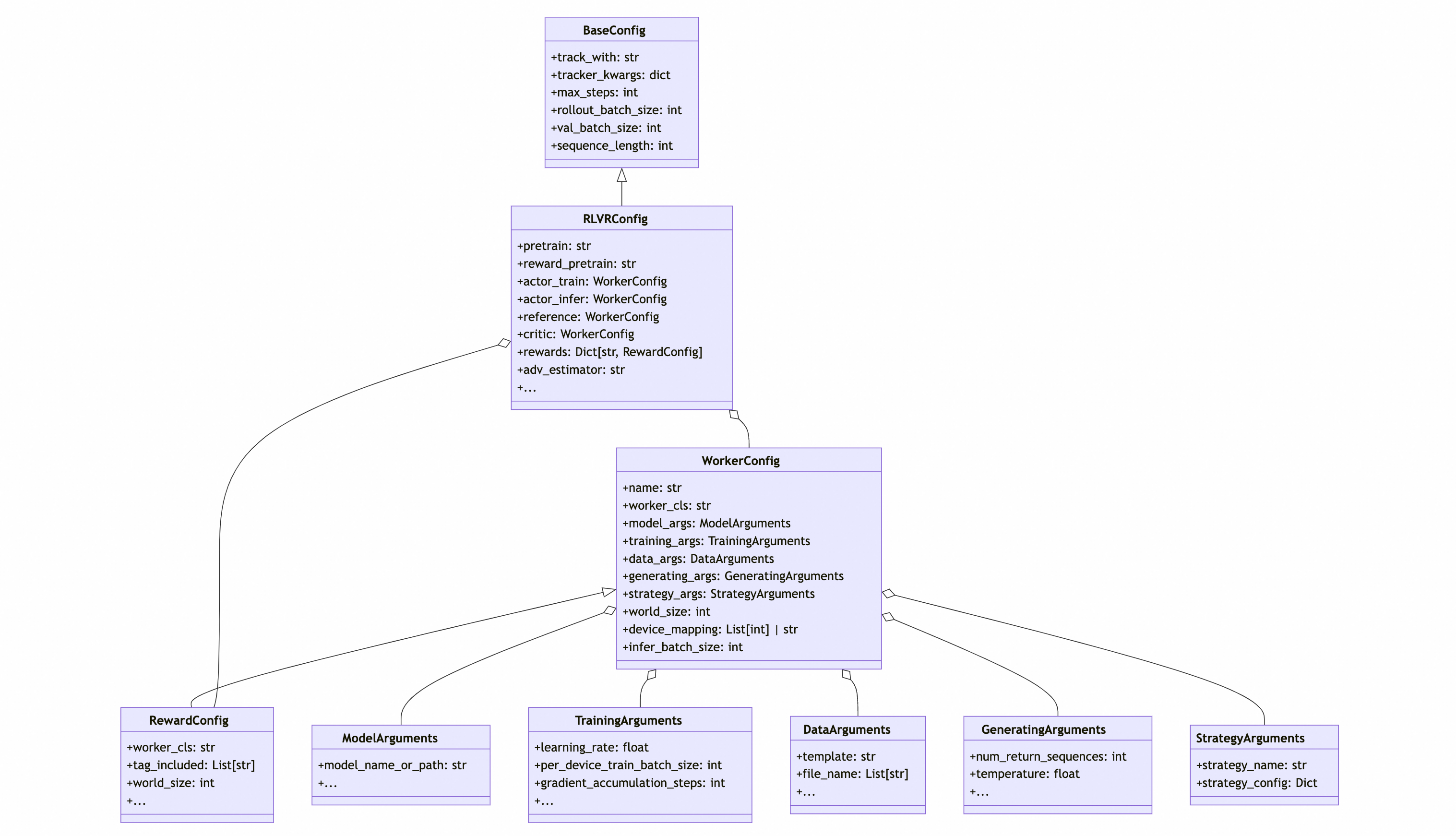
Configuration Class UML Diagram
To better understand ROLL's configuration system, the UML diagram of RLVRConfig is shown below:
- BaseConfig provides the most basic configuration keys, and specific application PipelineConfigs inherit from BaseConfig
- In PipelineConfig, multiple WorkerConfigs can be defined according to application needs. WorkerConfigs are independent and can be freely assigned independent resources and training/inference backends
- In WorkerConfig, ModelArguments, TrainingArguments, GeneratingArguments, DataArguments, and backend StrategyArguments held by the role are defined as needed
- WorkerConfig can be extended as needed to construct new application configurations
Mapping between YAML Configuration and PipelineConfig
In ROLL, there is a direct mapping relationship between YAML configuration files and Python configuration classes:
- Top-level fields in the YAML file correspond to the attributes of
PipelineConfig->BaseConfig - Role configurations (such as
actor_train,actor_infer) correspond toWorkerConfiginstances, which correspond to the configuration of attribute classes inPipelineConfig - Sub-fields under each role (such as
model_args,training_args) correspond to the corresponding parameter class instances
For example, in the YAML file:
actor_train:
model_args:
disable_gradient_checkpointing: false
dtype: bf16
training_args:
learning_rate: 1.0e-6
per_device_train_batch_size: 1
Mapping to Python code:
config.actor_train.model_args.disable_gradient_checkpointing = False
config.actor_train.model_args.dtype = "bf16"
config.actor_train.training_args.learning_rate = 1.0e-6
config.actor_train.training_args.per_device_train_batch_size = 1
Configuration Validation Mechanism
ROLL's configuration system has strict validation mechanisms:
- Configuration items in YAML must be explicitly defined in the corresponding Config class to be used
- Configuration item validation is implemented through data class type annotations and metadata
- Additional logical validation is performed in the
__post_init__method
This design prevents configuration item confusion and ensures configuration consistency and correctness.
Global Environment Variables/Worker-Specific Environment Variables Configuration Entry
In the ROLL framework, environment variable settings are divided into two levels:
- Global Environment Variables: Configured on
pipeline_configwithsystem_envs, taking effect for all roles in the entire pipeline. - Worker-Specific Environment Variables: Configured in
system_envswithinworker_config, taking effect only when the Worker's Ray Actor is created.
Configuration Method
Global Environment Variable Configuration
Set the system_envs field at the top level of the YAML configuration file:
exp_name: "example-exp"
# Other basic configurations...
# Global environment variable settings
system_envs:
NVTE_TORCH_COMPILE: '0'
RAY_PROFILING: "1"
# Role configurations
actor_train:
# ...
Worker-Specific Environment Variable Configuration
Set the system_envs field in specific role configurations:
actor_train:
model_args:
# ...
training_args:
# ...
# Environment variables effective only for actor_train role
system_envs:
NVTE_TORCH_COMPILE: '0'
actor_infer:
model_args:
# ...
generating_args:
# ...
# Environment variables effective only for actor_infer role
system_envs:
NVTE_TORCH_COMPILE: '0'
Priority Rules
When global environment variables and role-specific environment variables conflict, role-specific environment variables have higher priority and will override global settings.
Through this hierarchical environment variable configuration method, the ROLL framework provides independent and flexible environment variable configuration capabilities to meet different Worker requirements.
Configuration Example Analysis
The following is a detailed analysis of the example_grpo.yaml configuration file:
# Basic configuration
exp_name: "qwen2.5-7B-rlvr-config" # Experiment name
seed: 42 # Random seed
logging_dir: ./output/logs # Log directory
output_dir: ./output # Output directory
# Checkpoint saving configuration
checkpoint_config:
type: file_system
output_dir: /data/cpfs_0/rl_examples/models/${exp_name}
# Tracker configuration
track_with: tensorboard # Using tensorboard for tracking
tracker_kwargs:
log_dir: /data/oss_bucket_0/rl_examples/llm/tensorboard/roll_exp/rlvr # Log directory
# GRPO algorithm-related configuration
rollout_batch_size: 64 # Rollout batch size
adv_estimator: "grpo" # Advantage estimator using GRPO
num_return_sequences_in_group: 8 # Number of sequences returned per group
# Sequence length configuration
prompt_length: 2048 # Prompt length
response_length: 4096 # Response length
# Training parameters
ppo_epochs: 1 # PPO optimization rounds
use_kl_loss: true # Use KL divergence loss
kl_loss_coef: 0.001 # KL loss coefficient
loss_agg_mode: "seq-mean-token-sum" # Loss aggregation mode
# Advantage calculation related
whiten_advantages: true # Whiten advantage values
advantage_clip: 2.0 # Advantage value clipping
dual_clip_loss: true # Use dual clipping loss
# Reward processing
reward_clip: 10 # Reward value clipping
# Model configuration
pretrain: Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B # Pretrained model path
reward_pretrain: Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B # Reward model path
# Role configurations
actor_train: # Training role
model_args:
disable_gradient_checkpointing: false # Enable gradient checkpointing
dtype: bf16 # Data type
training_args:
learning_rate: 1.0e-6 # Learning rate
per_device_train_batch_size: 1 # Training batch size per device
gradient_accumulation_steps: 32 # Gradient accumulation steps
strategy_args:
strategy_name: megatron_train # Using Megatron training strategy
strategy_config:
tensor_model_parallel_size: 1 # Tensor parallel size
pipeline_model_parallel_size: 1 # Pipeline parallel size
device_mapping: list(range(0,16)) # Device mapping
actor_infer: # Inference role
model_args:
disable_gradient_checkpointing: true # Disable gradient checkpointing
dtype: bf16 # Data type
generating_args:
max_new_tokens: ${response_length} # Maximum new tokens
temperature: 0.99 # Temperature parameter
strategy_args:
strategy_name: vllm # Using vLLM inference strategy
strategy_config:
gpu_memory_utilization: 0.8 # GPU memory utilization
device_mapping: list(range(0,12)) # Device mapping
# Reward model configuration
rewards:
math_rule: # Math rule reward
worker_cls: roll.pipeline.rlvr.rewards.math_rule_reward_worker.MathRuleRewardWorker # Worker class
model_args:
model_name_or_path: ${reward_pretrain} # Model path
tag_included: [deepmath_103k, aime] # Included tags
world_size: 8 # Number of worker nodes
Through the above analysis, users can better understand the structure and usage methods of the ROLL configuration system.